There are 47 PCV theory test Braking Systems questions. You must get 85% (40 out of 47) to pass the test. You may review answers after each question by clicking the 'check answer' button or you can wait until the end of the test for your final score. Good luck!
PCV Theory Test Categories (2024)
Test Quick View
Click question box to reveal the correct answer. You can print these questions out by clicking the printer icon.
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: When your steering wheels are locked - as can happen in a skid - you can't steer the vehicle. Anti-lock brakes help you to keep steering control while you're braking heavily, but they aren't a substitute for good forward planning. Anticipation and planning ahead will minimise the risk of skidding more effectively than relying on your braking system.
Explanation: When your steering wheels are locked - as can happen in a skid - you can't steer the vehicle. Anti-lock brakes help you to keep steering control while you're braking heavily, but they aren't a substitute for good forward planning. Anticipation and planning ahead will minimise the risk of skidding more effectively than relying on your braking system.
2. What could prevent air pressure from building up in an air-brake system in frosty weather?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: When air is compressed, moisture condenses and collects in the air tanks. This can find its way along the network of pipes connected to the brakes. In frosty weather, the moisture can freeze in the pipes, blocking them completely. On modern vehicles, the air is dried before it's compressed and the air tanks drain automatically to shed any moisture. On older vehicles, the air tanks need draining manually.
Explanation: When air is compressed, moisture condenses and collects in the air tanks. This can find its way along the network of pipes connected to the brakes. In frosty weather, the moisture can freeze in the pipes, blocking them completely. On modern vehicles, the air is dried before it's compressed and the air tanks drain automatically to shed any moisture. On older vehicles, the air tanks need draining manually.
3. What should you do if the brake air-pressure warning light comes on while you're driving?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: When a warning light or device indicating a loss of brake pressure comes on, you must stop safely and get the fault put right immediately. The safety of you, your load, your passengers and all other road users is at risk.
Explanation: When a warning light or device indicating a loss of brake pressure comes on, you must stop safely and get the fault put right immediately. The safety of you, your load, your passengers and all other road users is at risk.
4. You've just started the engine. What must you do if the brake air-pressure warning light is showing?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Even though the warning light is showing, there may be sufficient pressure to release the parking brake. However, you mustn't do this, because there may not be enough air pressure to operate the service brake.
Explanation: Even though the warning light is showing, there may be sufficient pressure to release the parking brake. However, you mustn't do this, because there may not be enough air pressure to operate the service brake.
5. Your vehicle is fitted with an anti-lock braking system. What's it designed to allow you to do?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: Anti-lock braking systems sense when the wheels are about to lock. The sensor control releases the brakes and immediately applies them again. It will do this many times per second. This both prevents skidding and enables the driver to steer - something that's impossible when the steering wheels are skidding.
Explanation: Anti-lock braking systems sense when the wheels are about to lock. The sensor control releases the brakes and immediately applies them again. It will do this many times per second. This both prevents skidding and enables the driver to steer - something that's impossible when the steering wheels are skidding.
6. Your vehicle is fitted with an anti-lock braking system. When should you check that it's working properly?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: Modern anti-lock braking systems rely on electronics for their operation. A warning light on the dashboard shows that the system is operating. This light will usually go out when the vehicle reaches about 6 mph (10 km/h).
Explanation: Modern anti-lock braking systems rely on electronics for their operation. A warning light on the dashboard shows that the system is operating. This light will usually go out when the vehicle reaches about 6 mph (10 km/h).
7. What will 'pumping' the brake pedal in a vehicle fitted with anti-lock brakes cause?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: Before driving a vehicle fitted with anti-lock brakes, refer to the handbook. This will give you details of the manufacturer's recommended method of use. Remember, anti-lock brakes will enhance your skills, but they can't replace them.
Explanation: Before driving a vehicle fitted with anti-lock brakes, refer to the handbook. This will give you details of the manufacturer's recommended method of use. Remember, anti-lock brakes will enhance your skills, but they can't replace them.
8. You're driving a vehicle fitted with anti-lock brakes. What should you do when braking in an emergency?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Applying a firm, continuous brake pressure will enable the anti-lock braking system (ABS) to function properly. However, ABS is becoming increasingly sophisticated, so you should read the vehicle manufacturer's handbook for its advice about using the system.
Explanation: Applying a firm, continuous brake pressure will enable the anti-lock braking system (ABS) to function properly. However, ABS is becoming increasingly sophisticated, so you should read the vehicle manufacturer's handbook for its advice about using the system.
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Continually using the brakes could cause them to overheat. When that happens, they become less effective. This is called brake fade, and it occurs most often when the driver has to control the vehicle's speed on a long downhill gradient. To help prevent brake fade, use the endurance brake (retarder) and a lower gear to keep the vehicle's speed in check, rather than the wheel-mounted brakes.
Explanation: Continually using the brakes could cause them to overheat. When that happens, they become less effective. This is called brake fade, and it occurs most often when the driver has to control the vehicle's speed on a long downhill gradient. To help prevent brake fade, use the endurance brake (retarder) and a lower gear to keep the vehicle's speed in check, rather than the wheel-mounted brakes.
10. Brake fade' is a loss of effectiveness of the brakes when they overheat. When would 'brake fade' be most likely to happen?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Continuous use of the brakes will cause them to overheat, and in extreme cases they'll become ineffective. When you're going downhill, the momentum of your vehicle will cause you to gather speed very quickly. Use the endurance brake (retarder) and stay in a low gear to reduce the need to use the brakes.
Explanation: Continuous use of the brakes will cause them to overheat, and in extreme cases they'll become ineffective. When you're going downhill, the momentum of your vehicle will cause you to gather speed very quickly. Use the endurance brake (retarder) and stay in a low gear to reduce the need to use the brakes.
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: When approaching a long hill, you should take note of any early warning signs. Reduce your speed and select the appropriate gear in good time. Using an endurance brake (retarder), if fitted, will help control your speed.
Explanation: When approaching a long hill, you should take note of any early warning signs. Reduce your speed and select the appropriate gear in good time. Using an endurance brake (retarder), if fitted, will help control your speed.
B
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Anti-lock brakes are a driver aid, and can help you maintain steering control while braking. However, you mustn't rely on them to get you out of trouble or expect to be able to make sudden direction changes if you're going too fast.
Explanation: Anti-lock brakes are a driver aid, and can help you maintain steering control while braking. However, you mustn't rely on them to get you out of trouble or expect to be able to make sudden direction changes if you're going too fast.
13. Your vehicle has anti-lock brakes. How does this affect you when you're braking normally?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Plan well ahead to enable you to brake normally. Don't rely on anti-lock brakes to compensate for deficiencies in your driving.
Explanation: Plan well ahead to enable you to brake normally. Don't rely on anti-lock brakes to compensate for deficiencies in your driving.
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: An escape lane is for use in emergencies, usually when brakes have become hot and faded or failed completely while descending a long, steep hill. A sign will show you the direction of the road, and a chequered area, usually straight ahead, defines the escape route.
Explanation: An escape lane is for use in emergencies, usually when brakes have become hot and faded or failed completely while descending a long, steep hill. A sign will show you the direction of the road, and a chequered area, usually straight ahead, defines the escape route.
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: Escape lanes are found on steep downhill sections of road. They're designed to give a 'run-off' area, usually straight ahead, to allow vehicles to stop in an emergency. This is usually when brakes have faded or failed on large vehicles.
Explanation: Escape lanes are found on steep downhill sections of road. They're designed to give a 'run-off' area, usually straight ahead, to allow vehicles to stop in an emergency. This is usually when brakes have faded or failed on large vehicles.
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: Plan ahead and use your endurance brake (retarder) to help keep your speed in check on long downhill gradients. This can help to prevent your brakes from overheating and fading.
Explanation: Plan ahead and use your endurance brake (retarder) to help keep your speed in check on long downhill gradients. This can help to prevent your brakes from overheating and fading.
17. You're driving down a long hill. What should you use to prevent the brakes from overheating?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Endurance brakes or 'retarders' help to control a vehicle's speed. They operate by applying resistance to slow the vehicle without using the wheel brakes, so avoiding brake fade. The methods used include: increased engine braking, exhaust braking and transmission-mounted devices.
Explanation: Endurance brakes or 'retarders' help to control a vehicle's speed. They operate by applying resistance to slow the vehicle without using the wheel brakes, so avoiding brake fade. The methods used include: increased engine braking, exhaust braking and transmission-mounted devices.
B
C
D
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: Large vehicles can be fitted with various types of endurance brake (retarder). Make sure you're familiar with how the system operates on the vehicle you're using. Don't risk a crash or collision through ignorance.
Explanation: Large vehicles can be fitted with various types of endurance brake (retarder). Make sure you're familiar with how the system operates on the vehicle you're using. Don't risk a crash or collision through ignorance.
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: An endurance brake can help to control your speed on long downhill slopes without using the service brake. Reducing the use of the service brake helps to prevent the brakes from overheating and reduces the risk of brake fade.
Explanation: An endurance brake can help to control your speed on long downhill slopes without using the service brake. Reducing the use of the service brake helps to prevent the brakes from overheating and reduces the risk of brake fade.
20. Your vehicle is fully loaded. Where should you be braking when dealing with bends?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: When a vehicle changes direction, forces are applied to the vehicle and its load. Braking at the same time can result in additional forces being introduced, and this can lead to a loss of control. For this reason, braking should be carried out while driving in a straight line, so preventing these forces from acting together.
Explanation: When a vehicle changes direction, forces are applied to the vehicle and its load. Braking at the same time can result in additional forces being introduced, and this can lead to a loss of control. For this reason, braking should be carried out while driving in a straight line, so preventing these forces from acting together.
21. A lorry is overtaking you on a two-lane motorway. What should you do if it doesn't have the speed to get past?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Always be prepared to give way to overtaking lorries or buses. Maintaining your speed will only block the motorway to other traffic unnecessarily. You may find yourself in a similar situation if the limiter on your vehicle doesn't allow you enough speed to successfully overtake another vehicle.
Explanation: Always be prepared to give way to overtaking lorries or buses. Maintaining your speed will only block the motorway to other traffic unnecessarily. You may find yourself in a similar situation if the limiter on your vehicle doesn't allow you enough speed to successfully overtake another vehicle.
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: If you have to drive through a flood, do so with caution. Once out of the flood, you need to test your brakes to make sure they're working properly. To do this, check what's behind you, then drive in a low gear with the brakes gently applied.
Explanation: If you have to drive through a flood, do so with caution. Once out of the flood, you need to test your brakes to make sure they're working properly. To do this, check what's behind you, then drive in a low gear with the brakes gently applied.
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Air-brake systems rely on an engine-driven compressor to keep the reservoir tanks at their operating pressure. Coasting downhill and relying on the brakes to control your speed could result in the loss of sufficient air pressure to operate the brakes effectively.
Explanation: Air-brake systems rely on an engine-driven compressor to keep the reservoir tanks at their operating pressure. Coasting downhill and relying on the brakes to control your speed could result in the loss of sufficient air pressure to operate the brakes effectively.
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Continuous use of the brakes can result in them overheating and losing their effectiveness. This is known as 'brake fade' and it's most likely on long downhill gradients.
Explanation: Continuous use of the brakes can result in them overheating and losing their effectiveness. This is known as 'brake fade' and it's most likely on long downhill gradients.
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: Brake fade occurs when the brakes overheat. Good forward planning and correct use of the gears when descending hills, together with proper use of the endurance brake (retarder), can help to prevent brake fade.
Explanation: Brake fade occurs when the brakes overheat. Good forward planning and correct use of the gears when descending hills, together with proper use of the endurance brake (retarder), can help to prevent brake fade.
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Continuous use of the brakes on a long downhill gradient can cause them to overheat and become ineffective. This is called brake fade. You should use a low gear to enable the engine's braking effect to help control your speed. Also use the vehicle's retarder, if fitted. As well as reducing the likelihood of brake fade, this helps to keep air pressure in the tanks.
Explanation: Continuous use of the brakes on a long downhill gradient can cause them to overheat and become ineffective. This is called brake fade. You should use a low gear to enable the engine's braking effect to help control your speed. Also use the vehicle's retarder, if fitted. As well as reducing the likelihood of brake fade, this helps to keep air pressure in the tanks.
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: The endurance brake (retarder) slows the vehicle without the use of the wheel-mounted brakes. However, care should be taken in slippery conditions, when the retarder's effect can be powerful enough to cause a skid.
Explanation: The endurance brake (retarder) slows the vehicle without the use of the wheel-mounted brakes. However, care should be taken in slippery conditions, when the retarder's effect can be powerful enough to cause a skid.
28. You're stationary. The brake air-pressure warning light comes on. Why should you keep the parking brake on?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Even though a warning device indicates low air-brake pressure, you may still be able to release the parking brake. If you do this and start moving, the service brake may be ineffective and you may not be able to stop.
Explanation: Even though a warning device indicates low air-brake pressure, you may still be able to release the parking brake. If you do this and start moving, the service brake may be ineffective and you may not be able to stop.
29. You're about to drive a vehicle fitted with air-assisted hydraulic brakes. Why might the brake pedal feel hard when you press it?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: If the brake pedal is hard to press, this could mean a loss of vacuum or a fault in the vacuum pump. You shouldn't drive the vehicle until the fault has been repaired.
Explanation: If the brake pedal is hard to press, this could mean a loss of vacuum or a fault in the vacuum pump. You shouldn't drive the vehicle until the fault has been repaired.
30. Your vehicle is fitted with an air-assisted hydraulic braking system. What would warn you that the vacuum pump isn't working?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: The pump creates a vacuum in the servo unit. This reduces the amount of pressure you need to apply to the brake pedal. Without this vacuum, it's extremely difficult to press the brake pedal down.
Explanation: The pump creates a vacuum in the servo unit. This reduces the amount of pressure you need to apply to the brake pedal. Without this vacuum, it's extremely difficult to press the brake pedal down.
31. Your vehicle is fitted with hydraulic brakes. Why might the brake pedal go down too far when it's pressed?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: A loose brake pedal would suggest a serious loss of fluid from the hydraulic system. Don't drive your vehicle until the fault has been checked and fixed by a qualified person.
Explanation: A loose brake pedal would suggest a serious loss of fluid from the hydraulic system. Don't drive your vehicle until the fault has been checked and fixed by a qualified person.
32. You're about to drive a vehicle fitted with hydraulic brakes. What should you check before driving the vehicle?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: It's important to check all fluid levels during your daily checks, but it's especially important to remember the hydraulic fluid reservoir. A loss of fluid could lead to brake failure.
Explanation: It's important to check all fluid levels during your daily checks, but it's especially important to remember the hydraulic fluid reservoir. A loss of fluid could lead to brake failure.
33. Your vehicle is fitted with air-assisted hydraulic brakes. What would warn you that there isn't enough air in the system?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: If a warning buzzer or light alerts you to a loss of air pressure, you should stop on the side of the road immediately. You should have enough air in reserve to allow you to do this safely. Don't start or continue your journey until the fault has been repaired.
Explanation: If a warning buzzer or light alerts you to a loss of air pressure, you should stop on the side of the road immediately. You should have enough air in reserve to allow you to do this safely. Don't start or continue your journey until the fault has been repaired.
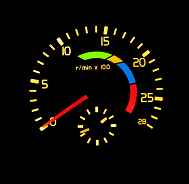
B
C
D
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: There are usually four coloured bands on the rev counter: green, amber, blue and red. The blue band will allow you to make the best use of engine braking. Try to keep in this band when going down a steep hill.
Explanation: There are usually four coloured bands on the rev counter: green, amber, blue and red. The blue band will allow you to make the best use of engine braking. Try to keep in this band when going down a steep hill.
35. Your vehicle is fitted with air brakes. What does it mean if a brake warning light shows when you've just started the engine?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: It's dangerous to drive a vehicle with low air pressure. To alert you to this, all vehicles are fitted with a warning light and/or buzzer. Don't move your vehicle if this warning shows or sounds.
Explanation: It's dangerous to drive a vehicle with low air pressure. To alert you to this, all vehicles are fitted with a warning light and/or buzzer. Don't move your vehicle if this warning shows or sounds.
36. Your vehicle is fitted with air-assisted hydraulic brakes. What fault would you suspect if the brake pedal becomes hard to press?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: A fault in the vacuum pump could be the cause of a stiff brake pedal. There could also be a leaking connection allowing air into the vacuum. Don't continue your journey until the fault has been fixed.
Explanation: A fault in the vacuum pump could be the cause of a stiff brake pedal. There could also be a leaking connection allowing air into the vacuum. Don't continue your journey until the fault has been fixed.
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: By using a retarder, the life of the brake linings is extended. This is because a retarder works by slowing the vehicle without using the wheel-mounted brakes.
Explanation: By using a retarder, the life of the brake linings is extended. This is because a retarder works by slowing the vehicle without using the wheel-mounted brakes.
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: Air-brake systems are fitted with a warning device that operates if the air pressure in the tanks drops below a safe level. There may be a warning buzzer and/or pressure gauges. You must be aware of the function of all gauges on your vehicle, and check them as you drive.
Explanation: Air-brake systems are fitted with a warning device that operates if the air pressure in the tanks drops below a safe level. There may be a warning buzzer and/or pressure gauges. You must be aware of the function of all gauges on your vehicle, and check them as you drive.
39. You're driving down a snow-covered hill. Why should you take care when using an independent endurance brake (retarder)?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Select an appropriate gear in good time and, if your vehicle has a dashboard-mounted lever, apply the endurance brake (retarder) in stages. Braking too much, too soon may result in locking your drive wheels.
Explanation: Select an appropriate gear in good time and, if your vehicle has a dashboard-mounted lever, apply the endurance brake (retarder) in stages. Braking too much, too soon may result in locking your drive wheels.
40. What should you avoid when using an independent endurance brake (retarder) on slippery roads?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: The endurance brake (retarder) usually operates by applying resistance, via the transmission, to the vehicle's driven wheels. If the road is slippery, the tyres may lose grip and the wheels will lock.
Explanation: The endurance brake (retarder) usually operates by applying resistance, via the transmission, to the vehicle's driven wheels. If the road is slippery, the tyres may lose grip and the wheels will lock.
41. You're about to drive an unfamiliar vehicle. What should you do if you think there may be moisture in the air-brake reservoir?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Moisture in the braking system can cause serious problems, especially in cold weather, when it could freeze and stop the brakes from working. Most modern vehicles have a system that drains automatically, but make sure you know which system is fitted to any vehicle that you drive.
Explanation: Moisture in the braking system can cause serious problems, especially in cold weather, when it could freeze and stop the brakes from working. Most modern vehicles have a system that drains automatically, but make sure you know which system is fitted to any vehicle that you drive.
42. You're about to start a journey in very frosty weather. What's the likely cause of low air-brake pressure?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Air-brake systems use air from the atmosphere, which contains moisture. The moisture condenses under pressure, resulting in water in the system. Make sure the air tanks are drained daily to remove any water and to help prevent the system from freezing in cold weather.
Explanation: Air-brake systems use air from the atmosphere, which contains moisture. The moisture condenses under pressure, resulting in water in the system. Make sure the air tanks are drained daily to remove any water and to help prevent the system from freezing in cold weather.
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Every vehicle fitted with anti-lock brakes must have a warning light in the cab of the vehicle. The warnings may differ between manufacturers, but on all types the warning light should come on when the ignition is switched on, and turn off when the vehicle reaches a speed of 6 mph (10 km/h). If the light stays on, there may be a fault; you should have the brakes checked before continuing your journey.
Explanation: Every vehicle fitted with anti-lock brakes must have a warning light in the cab of the vehicle. The warnings may differ between manufacturers, but on all types the warning light should come on when the ignition is switched on, and turn off when the vehicle reaches a speed of 6 mph (10 km/h). If the light stays on, there may be a fault; you should have the brakes checked before continuing your journey.
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: The most powerful and effective brake on the vehicle is the service brake, and this should be used in normal circumstances. Well-maintained brakes should apply an even pressure to all the wheels, providing an efficient, controlled stop.
Explanation: The most powerful and effective brake on the vehicle is the service brake, and this should be used in normal circumstances. Well-maintained brakes should apply an even pressure to all the wheels, providing an efficient, controlled stop.
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: As with stopping in any other situation, if you have to make a stop on an uphill gradient, wait until the vehicle has come to a halt before applying the parking brake.
Explanation: As with stopping in any other situation, if you have to make a stop on an uphill gradient, wait until the vehicle has come to a halt before applying the parking brake.
46. You're about to move off in a vehicle that has automatic transmission. What must you do before you select 'D' (drive)?
Mark one answer
B
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: It's important to apply the footbrake before you engage 'D' (or drive), so your vehicle doesn't creep forward or roll back out of control when you're about to move away. This can be dangerous; for example, if there's another road user close behind.
Explanation: It's important to apply the footbrake before you engage 'D' (or drive), so your vehicle doesn't creep forward or roll back out of control when you're about to move away. This can be dangerous; for example, if there's another road user close behind.
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: The way you drive matters. The safety and comfort of your passengers is your priority; if you have the correct attitude when you're driving, your passengers will be assured of a comfortable and pleasant journey. Good forward planning and anticipation will help you avoid having to turn or brake suddenly.
Explanation: The way you drive matters. The safety and comfort of your passengers is your priority; if you have the correct attitude when you're driving, your passengers will be assured of a comfortable and pleasant journey. Good forward planning and anticipation will help you avoid having to turn or brake suddenly.
















